Welcome to django-postgresql-dag’s documentation!¶
Contents¶
Quickstart Example¶
models.py¶
from django.db import models
from django_postgresql_dag.models import node_factory, edge_factory
class EdgeSet(models.Model):
# Not required, but provides a convenient way of grouping Edges
name = models.CharField(max_length=100, unique=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class NodeSet(models.Model):
# Not required, but provides a convenient way of grouping Nodes
name = models.CharField(max_length=100, unique=True)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
class NetworkEdge(edge_factory("NetworkNode", concrete=False)):
name = models.CharField(max_length=100, unique=True)
edge_set = models.ForeignKey(
EdgeSet,
on_delete=models.CASCADE,
null=True,
blank=True,
related_name="edge_set_edges",
)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
def save(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.name = f"{self.parent.name} {self.child.name}"
super().save(*args, **kwargs)
class NetworkNode(node_factory(NetworkEdge)):
name = models.CharField(max_length=100)
node_set = models.ForeignKey(
NodeSet,
on_delete=models.CASCADE,
null=True,
blank=True,
related_name="node_set_nodes",
)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
Optional arguments on the Edge model¶
`disable_circular_check`: Defaults to False. If set to True,
django-postgresql-dag will not check for circular paths. Essentially,
the resulting graph may no longer be a DAG.
`allow_duplicate_edges`: Defaults to True. Determines whether two
nodes are allowed to have more than one Edge directly connecting them.
Add some Instances via the Shell (or in views, etc)¶
>>> from myapp.models import NetworkNode, NetworkEdge
>>> root = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="root")
>>> a1 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="a1")
>>> a2 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="a2")
>>> a3 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="a3")
>>> b1 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="b1")
>>> b2 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="b2")
>>> b3 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="b3")
>>> b4 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="b4")
>>> c1 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="c1")
>>> c2 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="c2")
>>> root.add_child(a1)
>>> root.add_child(a2)
>>> a3.add_parent(root) # You can add from either side of the relationship
>>> b1.add_parent(a1)
>>> a1.add_child(b2)
>>> a2.add_child(b2)
>>> a3.add_child(b3)
>>> a3.add_child(b4)
>>> b3.add_child(c2)
>>> b3.add_child(c1)
>>> b4.add_child(c1)
Add Edges and Nodes to EdgeSet and NodeSet models (FK)¶
>>> y = EdgeSet.objects.create()
>>> y.save()
>>> c1_ancestors = c1.ancestors_edges()
>>> for ancestor in c1_ancestors:
>>> ancestor.edge_set = y
>>> ancestor.save()
>>> x = NodeSet.objects.create()
>>> x.save()
>>> root.node_set = x
>>> root.save()
>>> a1.node_set = x
>>> a1.save()
>>> b1.node_set = x
>>> b1.save()
>>> b2.node_set = x
>>> b2.save()
Resulting Database Tables¶
myapp_networknode¶
id | name
----+------
1 | root
2 | a1
3 | a2
4 | a3
5 | b1
6 | b2
7 | b3
8 | b4
9 | c1
10 | c2
myapp_networkedge¶
id | child_id | parent_id | name
----+----------+-----------+---------
1 | 2 | 1 | root a1
2 | 3 | 1 | root a2
3 | 4 | 1 | root a3
4 | 5 | 2 | a1 b1
5 | 6 | 2 | a1 b2
6 | 6 | 3 | a2 b2
7 | 7 | 4 | a3 b3
8 | 8 | 4 | a3 b4
9 | 10 | 7 | b3 c2
10 | 9 | 7 | b3 c1
11 | 9 | 8 | b4 c1
Diagramatic View¶
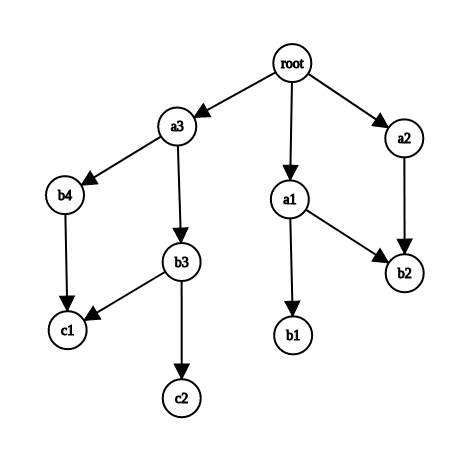
Work with the Graph in the Shell (or in views, etc)¶
>>> from myapp.models import NetworkNode, NetworkEdge
# Descendant methods which return a queryset
>>> root.descendants()
<QuerySet [<NetworkNode: a1>, <NetworkNode: a2>, <NetworkNode: a3>, <NetworkNode: b1>, <NetworkNode: b2>, <NetworkNode: b3>, <NetworkNode: b4>, <NetworkNode: c1>, <NetworkNode: c2>]>
>>> root.descendants(max_depth=1)
<QuerySet [<NetworkNode: a1>, <NetworkNode: a2>, <NetworkNode: a3>]>
>>> root.self_and_descendants()
<QuerySet [<NetworkNode: root>, <NetworkNode: a1>, <NetworkNode: a2>, <NetworkNode: a3>, <NetworkNode: b1>, <NetworkNode: b2>, <NetworkNode: b3>, <NetworkNode: b4>, <NetworkNode: c1>, <NetworkNode: c2>]>
>>> root.descendants_and_self()
[<NetworkNode: c2>, <NetworkNode: c1>, <NetworkNode: b4>, <NetworkNode: b3>, <NetworkNode: b2>, <NetworkNode: b1>, <NetworkNode: a3>, <NetworkNode: a2>, <NetworkNode: a1>, <NetworkNode: root>]
# Ancestor methods which return a queryset
>>> c1.ancestors()
<QuerySet [<NetworkNode: root>, <NetworkNode: a3>, <NetworkNode: b3>, <NetworkNode: b4>]>
>>> c1.ancestors(max_depth=2)
<QuerySet [<NetworkNode: a3>, <NetworkNode: b3>, <NetworkNode: b4>]>
>>> c1.ancestors_and_self()
<QuerySet [<NetworkNode: root>, <NetworkNode: a3>, <NetworkNode: b3>, <NetworkNode: b4>, <NetworkNode: c1>]>
>>> c1.self_and_ancestors()
[<NetworkNode: c1>, <NetworkNode: b4>, <NetworkNode: b3>, <NetworkNode: a3>, <NetworkNode: root>]
# Get the node's clan (all ancestors, self, and all descendants)
>>> b3.clan()
<QuerySet [<NetworkNode: root>, <NetworkNode: a3>, <NetworkNode: b3>, <NetworkNode: c1>, <NetworkNode: c2>]>
# Get all roots or leaves associated with the node
>>> b3.roots()
{<NetworkNode: root>}
>>> b3.leaves()
{<NetworkNode: c1>, <NetworkNode: c2>}
# Perform path search
>>> root.path(c1)
<QuerySet [<NetworkNode: root>, <NetworkNode: a3>, <NetworkNode: b3>, <NetworkNode: c1>]>
>>> root.path(c1, max_depth=2) # c1 is 3 levels deep from root
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<input>", line 1, in <module>
root.path(c1, max_depth=2)
File "/home/runner/pgdagtest/pg/models.py", line 550, in path
ids = [item.id for item in self.path_raw(target_node, **kwargs)]
File "/home/runner/pgdagtest/pg/models.py", line 546, in path_raw
raise NodeNotReachableException
pg.models.NodeNotReachableException
>>> root.path(c1, max_depth=3)
<QuerySet [<NetworkNode: root>, <NetworkNode: a3>, <NetworkNode: b3>, <NetworkNode: c1>]>
# Reverse (upward) path search
>>> c1.path(root) # Path defaults to top-down search, unless `directional` is set to False
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<input>", line 1, in <module>
c1.path(root)
File "/home/runner/pgdagtest/pg/models.py", line 548, in path
ids = [item.id for item in self.path_raw(target_node, **kwargs)]
File "/home/runner/pgdagtest/pg/models.py", line 544, in path_raw
raise NodeNotReachableException
pg.models.NodeNotReachableException
>>> c1.path(root, directional=False)
<QuerySet [<NetworkNode: c1>, <NetworkNode: b3>, <NetworkNode: a3>, <NetworkNode: root>]>
>>> root.distance(c1)
3
# Check node properties
>>> root.is_root()
True
>>> root.is_leaf()
False
>>> root.is_island()
False
>>> c1.is_root()
False
>>> c1.is_leaf()
True
>>> c1.is_island()
False
# Get ancestors/descendants tree output
>>> a2.descendants_tree()
{<NetworkNode: b2>: {}}
>>> root.descendants_tree()
{<NetworkNode: a1>: {<NetworkNode: b1>: {}, <NetworkNode: b2>: {}}, <NetworkNode: a2>: {<NetworkNode: b2>: {}}, <NetworkNode: a3>: {<NetworkNode: b3>: {<NetworkNode: c2>: {}, <NetworkNode: c1>: {}}, <NetworkNode: b4>: <NetworkNode: c1>: {}}}}
>>> root.ancestors_tree()
{}
>>> c1.ancestors_tree()
{<NetworkNode: b3>: {<NetworkNode: a3>: {<NetworkNode: root>: {}}}, <NetworkNode: b4>: {<NetworkNode: a3>: {<NetworkNode: root>: {}}}}
>>> c2.ancestors_tree()
{<NetworkNode: b3>: {<NetworkNode: a3>: {<NetworkNode: root>: {}}}}
# Get a queryset of edges relatd to a particular node
>>> a1.ancestors_edges()
<QuerySet [<NetworkEdge: root a1>]>
>>> b4.descendants_edges()
<QuerySet [<NetworkEdge: b4 c1>]>
>>> b4.clan_edges()
<QuerySet [<NetworkEdge: root a3>, <NetworkEdge: a3 b4>, <NetworkEdge: b4 c1>]>
# Get the nodes at the start or end of an edge
>>> e1.parent
<NetworkNode: root>
>>> e1.child
<NetworkNode: a1>
>>> e2.parent
<NetworkNode: b4>
>>> e2.child
<NetworkNode: c1>
# Edge-specific Manager methods
>>> NetworkEdge.objects.descendants(b3)
<QuerySet [<NetworkEdge: b3 c2>, <NetworkEdge: b3 c1>]>
>>> NetworkEdge.objects.ancestors(b3)
<QuerySet [<NetworkEdge: root a3>, <NetworkEdge: a3 b3>]>
>>> NetworkEdge.objects.clan(b3)
<QuerySet [<NetworkEdge: root a3>, <NetworkEdge: a3 b3>, <NetworkEdge: b3 c2>, <NetworkEdge: b3 c1>]>
>>> NetworkEdge.objects.path(root, c1)
<QuerySet [<NetworkEdge: root a3>, <NetworkEdge: a3 b3>, <NetworkEdge: b3 c1>]>
>>> NetworkEdge.objects.path(c1, root) # Path defaults to top-down search, unless `directional` is set to False
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<input>", line 1, in <module>
NetworkEdge.objects.path(c1, root)
File "/home/runner/pgdagtest/pg/models.py", line 677, in path
start_node.path(end_node),
File "/home/runner/pgdagtest/pg/models.py", line 548, in path
ids = [item.id for item in self.path_raw(target_node, **kwargs)]
File "/home/runner/pgdagtest/pg/models.py", line 544, in path_raw
raise NodeNotReachableException
pg.models.NodeNotReachableException
>>> NetworkEdge.objects.path(c1, root, directional=False)
<QuerySet [<NetworkEdge: b3 c1>, <NetworkEdge: a3 b3>, <NetworkEdge: root a3>]>
Methods on Node and Edge¶
Listed below are the methods that are useful for building/manipulating/querying the graph. We ignore here the methods used only for internal functionality.
Node¶
Manager Methods¶
roots(self, node=None)
Returns a Queryset of all root nodes (nodes with no parents) in the Node model. If a node instance is specified, returns only the roots for that node.
leaves(self, node=None)
Returns a Queryset of all leaf nodes (nodes with no children) in the Node model. If a node instance is specified, returns only the leaves for that node.
Model Methods¶
Methods used for building/manipulating¶
add_child(self, child, **kwargs)
Provided with a Node instance, attaches that instance as a child to the current Node instance
remove_child(self, child, delete_node=False)
Removes the edge connecting this node to the provided child Node instance, and optionally deletes the child node as well
add_parent(self, parent, \*args, **kwargs)
Provided with a Node instance, attaches the current instance as a child to the provided Node instance
remove_parent(self, parent, delete_node=False)
Removes the edge connecting this node to parent, and optionally deletes the parent node as well
Methods used for querying¶
ancestors(self, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of all nodes in connected paths in a rootward direction
ancestors_count(self)
Returns an integer number representing the total number of ancestor nodes
self_and_ancestors(self, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of all nodes in connected paths in a rootward direction, prepending with self
ancestors_and_self(self, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of all nodes in connected paths in a rootward direction, appending with self
descendants(self, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of all nodes in connected paths in a leafward direction
descendants_count(self)
Returns an integer number representing the total number of descendant nodes
self_and_descendants(self, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of all nodes in connected paths in a leafward direction, prepending with self
descendants_and_self(self, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of all nodes in connected paths in a leafward direction, appending with self
clan(self, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet with all ancestors nodes, self, and all descendant nodes
clan_count(self)
Returns an integer number representing the total number of clan nodes
siblings(self)
Returns a QuerySet of all nodes that share a parent with this node, excluding self
siblings_count(self)
Returns count of all nodes that share a parent with this node
siblings_with_self(self)
Returns a QuerySet of all nodes that share a parent with this node and self
partners(self)
Returns a QuerySet of all nodes that share a child with this node, excluding self
partners_count(self)
Returns count of all nodes that share a child with this node
partners_with_self(self)
Returns a QuerySet of all nodes that share a child with this node and self
path_exists(self, ending_node, **kwargs)
Given an ending Node instance, returns a boolean value determining whether there is a path from the current Node instance to the ending Node instance
Optional keyword argument: directional (boolean: if True, path searching operates normally, in a leafward only direction. If False, search operates in both directions)
path(self, ending_node, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of the shortest path from self to ending node, optionally in either direction. The resulting Queryset is sorted from root-side, toward leaf-side, regardless of the relative position of starting and ending nodes.
Optional keyword argument: directional (boolean: if True, path searching operates normally, in a leafward only direction. If False, search operates in both directions)
distance(self, ending_node, **kwargs)
Returns the shortest hops count to the target node
is_root(self)
Returns True if the current Node instance has children, but no parents
is_leaf(self)
Returns True if the current Node instance has parents, but no children
is_island(self)
Returns True if the current Node instance has no parents nor children
is_ancestor_of(self, ending_node, **kwargs)
Provided an ending_node Node instance, returns True if the current Node instance and is an ancestor of the provided Node instance
Optional keyword argument: directional (boolean: if True, path searching operates normally, in a leafward only direction. If False, search operates in both directions)
is_descendant_of(self, ending_node, **kwargs)
Provided an ending_node Node instance, returns True if the current Node instance and is a descendant of the provided Node instance
Optional keyword argument: directional (boolean: if True, path searching operates normally, in a leafward only direction. If False, search operates in both directions)
is_sibling_of(self, ending_node)
Provided an ending_node Node instance, returns True if the provided Node instance and the current Node instance share a parent Node
is_partner_of(self, ending_node)
Provided an ending_node Node instance, returns True if the provided Node instance and the current Node instance share a child Node
node_depth(self)
Returns an integer representing the depth of this Node instance from furthest root
Not yet implemented
connected_graph(self, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of all nodes connected in any way to the current Node instance
descendants_tree(self)
Returns a tree-like structure with descendants for the current Node
ancestors_tree(self)
Returns a tree-like structure with ancestors for the current Node
roots(self)
Returns a QuerySet of all root nodes, if any, for the current Node
leaves(self)
Returns a QuerySet of all leaf nodes, if any, for the current Node
descendants_edges(self)
Returns a QuerySet of descendant Edge instances for the current Node
ancestors_edges(self)
Returns a QuerySet of ancestor Edge instances for the current Node
clan_edges(self)
Returns a QuerySet of all Edge instances associated with a given node
Edge¶
Manager Methods¶
from_nodes_queryset(self, nodes_queryset)
Provided a QuerySet of nodes, returns a QuerySet of all Edge instances where a parent and child Node are within the QuerySet of nodes
descendants(self, node, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of all Edge instances descended from the given Node instance
ancestors(self, node, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of all Edge instances which are ancestors of the given Node instance
clan(self, node, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of all Edge instances for ancestors, self, and descendants
path(self, start_node, end_node, **kwargs)
Returns a QuerySet of all Edge instances for the shortest path from start_node to end_node
validate_route(self, edges, **kwargs)
Given a list or set of Edge instances, verify that they result in a contiguous route
Not yet implemented.
sort(self, edges, **kwargs)
Given a list or set of Edge instances, sort them from root-side to leaf-side
Not yet implemented.
insert_node(self, edge, node, clone_to_rootside=False, clone_to_leafside=False, pre_save=None, post_save=None)
Inserts a node into an existing Edge instance. Returns a tuple of the newly created rootside_edge (parent to the inserted node) and leafside_edge (child to the inserted node).
Process: 1. Add a new Edge from the parent Node of the current Edge instance to the provided Node instance, optionally cloning properties of the existing Edge. 2. Add a new Edge from the provided Node instance to the child Node of the current Edge instance, optionally cloning properties of the existing Edge. 3. Remove the original Edge instance.
- The instance will still exist in memory, though not in database (https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.1/ref/models/instances/#refreshing-objects-from-database). Recommend running the following after conducting the deletion:
del instancename
Cloning will fail if a field has unique=True, so a pre_save function can be passed into this method. Likewise, a post_save function can be passed in to rebuild relationships. For instance, if you have a name field that is unique and generated automatically in the model’s save() method, you could pass in a the following pre_save function to clear the name prior to saving the new Edge instance(s):
def pre_save(new_edge):
new_edge.name = ""
return new_edge
A more complete example, where we have models named NetworkEdge & NetworkNode, and we want to insert a new Node (n2) into Edge e1, while copying e1’s field properties (except name) to the newly created rootside Edge instance (n1 to n2) is shown below.
Original Final
- n1 o n1 o
- o n2/
n3 o n3 o
from myapp.models import NetworkEdge, NetworkNode
n1 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="n1")
n2 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="n2")
n3 = NetworkNode.objects.create(name="n3")
# Connect n3 to n1
n1.add_child(n3)
e1 = NetworkEdge.objects.last()
# function to clear the `name` field, which is autogenerated and must be unique
def pre_save(new_edge):
new_edge.name = ""
return new_edge
NetworkEdge.objects.insert_node(e1, n2, clone_to_rootside=True, pre_save=pre_save)
Transformations¶
Provides various utilities for manipulating and transforming the graph data
Content pending…
View this project on Github.